 Here is AtlantisFiber’s non-biased analysis of Asphalt vs. Concrete.
Here is AtlantisFiber’s non-biased analysis of Asphalt vs. Concrete.
When it comes to paving surfaces, asphalt and concrete are two of the most frequently used materials. Both are popular due to their durability, strength, and appearance. However, when it comes to choosing between the two, the cost is often a significant factor. Determining which material is more cost-effective can be a complex process that requires consideration of various factors. In this article, we will provide a detailed cost analysis of asphalt and concrete, highlighting the factors that affect costs and identifying the most cost-effective option. Furthermore, we will examine the environmental impact, durability, maintenance, advantages, and disadvantages of both materials. Our goal is to provide a comprehensive guide for anyone looking to make an informed decision about paving surfaces in 2023.
Introduction to an Analysis of Asphalt vs Concrete
In the world of pavement, two materials reign supreme: asphalt and concrete. You’ve probably driven over both types of pavement countless times, but do you know the difference between them? In this article, we’ll take a deep dive into the world of asphalt & concrete and compare the costs and environmental impacts of each material.
Overview & History of Asphalt and Concrete
Asphalt and concrete are both used for paving roads, parking lots, and other surfaces. Asphalt is a black, sticky substance made from petroleum, while concrete is a mixture of cement, water, and aggregates such as gravel or sand. Asphalt is flexible and can handle temperature changes well, while concrete is more rigid and can withstand heavier loads.
Asphalt has been used for thousands of years, first as a waterproofing material for roofs and later as a paving material. Concrete dates back to ancient Rome, when it was used to build structures like the Colosseum. The first modern concrete road was built in 1909, while asphalt became popular in the 1920s.
 Analysis of Asphalt and Concrete Cost
Analysis of Asphalt and Concrete Cost
When it comes to choosing between asphalt and concrete for a paving project, the cost is a major factor. Let’s take a look at the cost comparison between the two materials.
Initial Investment & Life-Cycle Cost Analysis
In general, asphalt is cheaper to install than concrete. This is because it requires less labor and equipment, and the materials are less expensive. The average cost of asphalt paving is around $3 to $5 per square foot, while concrete typically costs between $7 to $10 per square foot.
While asphalt may be cheaper to install, it requires more maintenance than concrete. Asphalt needs to be sealed every three to five years, which can cost around $0.25 to $0.50 per square foot. Concrete, on the other hand, requires less maintenance and can last up to 30 years or more. When you factor in the cost of maintenance over the life of the pavement, concrete may actually be more cost-effective than asphalt.
Factors Affecting Asphalt and Concrete Cost
The cost of both asphalt and concrete can be affected by various factors, including material costs, labor costs, and equipment costs.
Material, Labor, and Equipment Costs Analysis
The cost of asphalt and concrete materials can vary depending on factors such as location, availability, and market demand. Asphalt is typically cheaper than concrete, but the cost of petroleum can affect the price of asphalt.
Labor costs for asphalt and concrete can also vary depending on location and market demand. In general, asphalt requires less labor than concrete since it can be installed more quickly.
Equipment costs for asphalt and concrete projects can also vary depending on the size and complexity of the project. Asphalt projects typically require less equipment than concrete projects, which can make it a more cost-effective option.
In addition to cost, it’s important to consider the environmental impact of asphalt and concrete. Let’s take a look at the greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption, and recyclability of each material.
 Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Energy Consumption, and Recyclability Analysis
Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Energy Consumption, and Recyclability Analysis
Asphalt production and transportation can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, while concrete production can produce carbon dioxide. However, some asphalt can be produced using recycled materials, which can reduce emissions.
Asphalt production requires less energy than concrete production, but asphalt needs to be heated at high temperatures during installation. Concrete production requires energy to produce cement, but once it’s installed it doesn’t require as much energy as asphalt.
Both asphalt and concrete can be recycled, but asphalt is more commonly recycled. Recycled asphalt can be used in new pavement, which can reduce the need for new materials and reduce waste. Concrete can also be recycled, but it’s less commonly done due to the cost of crushing and processing the material.
In conclusion, when comparing asphalt and concrete, it’s important to consider factors such as initial cost, life-cycle cost, environmental impact, and project-specific needs. While asphalt may be cheaper to install, concrete may be more cost-effective over the long term due to its reduced maintenance needs. Regardless of which material you choose, be sure to consider the environmental impact of your decision and look for ways to reduce waste and emissions.
Durability and Maintenance Analysis
When it comes to durability, both asphalt and concrete have their strengths and weaknesses. Asphalt is known for its flexibility, which allows it to withstand changes in temperature and prevent cracking. On the other hand, concrete is more rigid and less susceptible to deformation, making it a good choice for heavy-traffic areas.
Expected Lifespan & Maintenance Requirements of Asphalt and Concrete
When properly installed and maintained, asphalt can last anywhere from 20 to 30 years, while concrete can last up to 40 years or more. However, harsh weather conditions and heavy traffic can significantly reduce the lifespan of both materials.
Asphalt requires more frequent maintenance than concrete, including regular seal coating, crack filling, and patching. Concrete, on the other hand, is more resistant to cracking and deterioration but may require occasional joint sealing or repairs.
 Advantages and Disadvantages of Asphalt and Concrete
Advantages and Disadvantages of Asphalt and Concrete
Advantages of Asphalt
- Lower initial cost compared to concrete
- Faster installation time
- Better traction for vehicles and pedestrians
- Easier to repair and maintain
Disadvantages of Asphalt
- Requires more frequent maintenance and repair
- Can soften and deform in high temperatures
- Can be prone to cracks and potholes
- Not as environmentally friendly as concrete
Advantages of Concrete
- More durable and long-lasting than asphalt
- Resistant to harsh weather conditions and heavy traffic
- Requires less maintenance and repair
- More environmentally friendly than asphalt
Disadvantages of Concrete
- Higher initial cost compared to asphalt
- Longer installation time
- More prone to surface cracking
- Can be slippery when wet
Conclusion and Recommendations
Factors to Consider when Choosing between Asphalt and Concrete
When choosing between asphalt and concrete, there are several factors to consider, including:
- Budget and cost-effectiveness
- Climate and weather conditions
- Traffic volume and type of vehicles
- Maintenance and repair requirements
- Environmental impact
Summary of Cost and Environmental Analysis
While asphalt may have a lower initial cost, the frequent maintenance and repair required can add up over time. In terms of environmental impact, concrete is more sustainable and eco-friendly than asphalt.
Recommendations for Choosing Between Asphalt and Concrete
Overall, the choice between asphalt and concrete will depend on your specific needs and circumstances. For high-traffic areas, concrete may be the better choice due to its durability and long lifespan. However, for smaller projects and areas with lower traffic volume, asphalt may be a more cost-effective option. It is important to consider all factors carefully before making a decision.
In conclusion, the choice between asphalt and concrete is one that should be made thoughtfully and with careful consideration of a variety of factors. While cost is an important factor, it is not the only one that should be considered. By weighing the various advantages and disadvantages, as well as the environmental impact, durability, and maintenance requirements of each material, you can make an informed decision about which material to use. Ultimately, choosing the right material will ensure that your paving surface is not only cost-effective but also durable and sustainable.
FAQs
How do I determine whether to use asphalt or concrete for my pavement project?
The choice between asphalt and concrete depends on several factors, including cost, environmental impact, durability, maintenance requirements, and appearance. You should also consider the location and expected traffic volume of the pavement. Consulting with a professional contractor can help ensure that you make an informed decision.
Which is more cost-effective, asphalt or concrete?
The answer to this question depends on several factors, including material and labor costs, equipment requirements, and maintenance needs. While asphalt is often less expensive initially, concrete may be more cost-effective in the long run due to its durability and lower maintenance requirements.
What is the environmental impact of asphalt and concrete?
Both asphalt and concrete have environmental impacts, including greenhouse gas emissions and energy consumption. However, asphalt has a greater impact due to its petroleum-based composition. Concrete is more recyclable than asphalt, which makes it a more sustainable choice. AtlantisFiber™Concrete Admixtures, however, are designed to help decrease the impact of concrete.
How long can I expect my asphalt or concrete pavement to last?
The lifespan of asphalt and concrete pavement depends on several factors, including the quality of the installation, the amount of traffic, and the maintenance provided. Generally, properly installed and maintained asphalt pavement can last up to 20 years, while concrete can last up to 30 years or more. With AtlantisFiber’s performance advantages, we are looking to see a 50+ year cycle in moderate to extreme conditions.
We’d love to hear your opinion and your experiences; please visit us and leave your opinion on our LinkedIn page.
 Analysis of Asphalt and Concrete Cost
Analysis of Asphalt and Concrete Cost Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Energy Consumption, and Recyclability Analysis
Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Energy Consumption, and Recyclability Analysis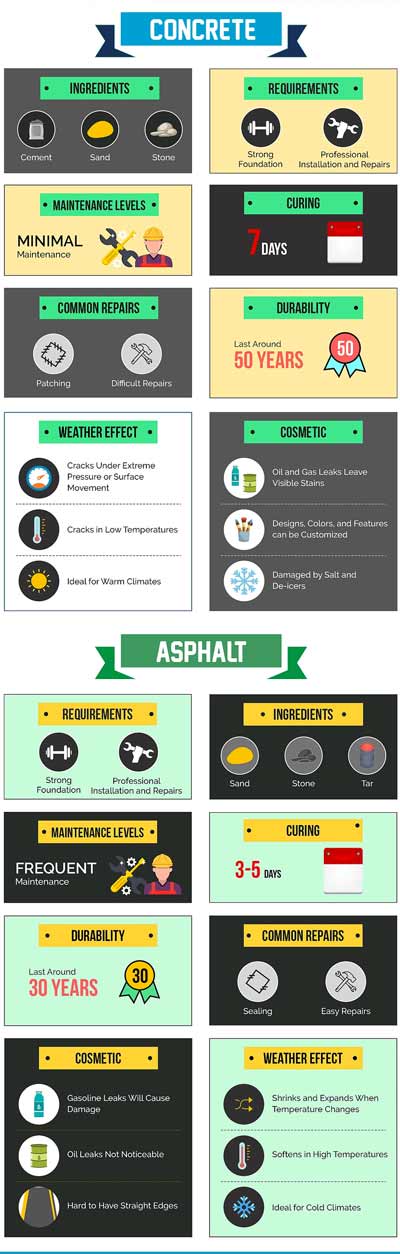 Advantages and Disadvantages of Asphalt and Concrete
Advantages and Disadvantages of Asphalt and Concrete